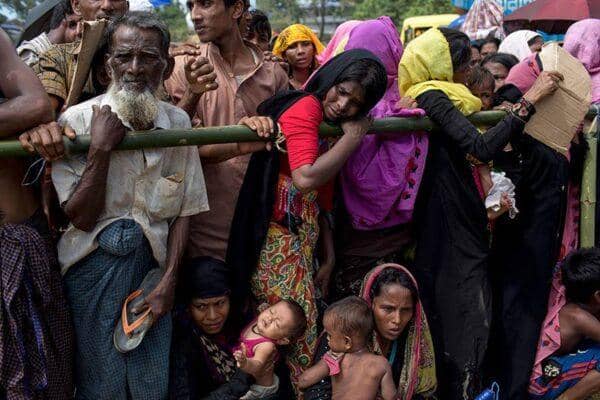
The beginning of the school year is always an exciting and challenging time for children and parents alike. However, for many children around the world, going back to school in 2023 is not a guarantee. They face many barriers and difficulties that prevent them from accessing quality education, such as poverty, conflict, displacement, discrimination, or lack of resources. In this article, we will show you how you can help these children go back to school in 2023 by donating for education with our Islamic charity institution.
Why Donate for Education?
Education is a basic human right and a key factor for social and economic development. It empowers individuals and communities, reduces poverty and inequality, promotes peace and justice, and fosters innovation and creativity. Education also has many benefits for both the giver and the receiver of charity. Here are some of the reasons why donating for education is a great deed that has many rewards in this life and the hereafter:
- Donating for education is a form of sadaqah jariyah (ongoing charity). This means that you will continue to receive rewards from Allah (SWT) as long as the beneficiary of your donation benefits from the education you provided.
- Donating for education is following the sunnah (tradition) of the Prophet Muhammad (SAW). He said: “The best of you are those who learn the Quran and teach it.” (Bukhari) He also said: “Whoever guides someone to goodness will have a reward like one who did it.” (Muslim)
- Donating for education is fulfilling the command of Allah (SWT). He said: “Read! In the name of your Lord who created – He created man from a clinging substance. Read! And your Lord is the most Generous – Who taught by the pen – He taught man that which he knew not.” (Quran 96:1-5) He also said: “And say: My Lord, increase me in knowledge.” (Quran 20:114)
- Donating for education is benefiting the ummah (community) and the humanity. Education can help solve many of the problems and challenges that we face today, such as ignorance, extremism, corruption, violence, disease, or environmental degradation. Education can also foster unity, cooperation, tolerance, compassion, and solidarity among people of different backgrounds, cultures, and faiths.
How to Donate for Education with Our Islamic Charity Institution?
Donating for education with our Islamic charity institution is not difficult or expensive. In fact, you can do it with just a few clicks and a small donation. Here is how you can donate for education with our Islamic charity institution:
- Visit our website and choose the “Donate for Education” option from our menu.
- Select the amount of money you want to donate and the type of education you want to support. We have different types of education programs that cater to different needs and levels of education, such as primary education, secondary education, higher education, vocational training, or Quranic education.
- If you are interested, you can enter your personal information. You can pay securely online using your Crypto Wallet.
- You will receive regular updates and reports on how your donation is making a difference in the lives of children and their families.
That’s it! You have just donated for education and earned yourself a share of the rewards of paradise. May Allah (SWT) accept your donation and bless you with His mercy and grace. Ameen.
What are the Impacts of Your Donation for Education?
Your donation for education can have a huge impact on the lives of children and their families. Here are some of the impacts that your donation can make:
- Your donation can help provide access to quality education for children who otherwise would not have it. This can include providing school fees, uniforms, books, stationery, transportation, or scholarships.
- Your donation can help improve the quality of education for children who already have access to it. This can include providing teacher training, curriculum development, learning materials, equipment, or infrastructure.
- Your donation can help support the holistic development of children through education. This can include providing health care, nutrition, hygiene, psychosocial support, life skills, or extracurricular activities.
- Your donation can help empower children through education. This can include providing opportunities for participation, leadership, advocacy, or entrepreneurship.
- Your donation can help transform the lives of children through education. This can include improving their academic performance, self-esteem, confidence, aspirations, employability, income, or well-being.
I hope this helps you understand how you can help children go back to school in 2023 by donating for education with our Islamic charity institution. If you have any questions or feedback, please feel free to contact us anytime. We would love to hear from you and assist you in any way we can.
Thank you for reading this article and supporting our Islamic charity institution. Please share this article with your friends and family and encourage them to donate for education too. Together, we can make a difference in the world and please Allah (SWT). JazakAllahu khairan.